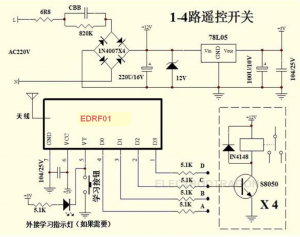
EDRF1
Features
- Smaller, more reliable RF receiver, high-performance MCU, EEPROM three-in-one chip
- Intelligent identification chip type, support EV1527, PT2262 and other learning code / fixed code (welding code) IC remote control mixed use
- Compatible with most learning codes and fixed code (welding code) chips in the market, including EV1527, PT2262, HX2262, SC2260, SC5211, HS2240, etc.
- Intelligently adapt to the oscillating resistance of the transmitting end, no need to consider the oscillating resistance of the transmitting end, it is versatile and easy to use
- Good local oscillator radiation suppression capability, multiple modules can work together without interfering with each other, without affecting the receiving distance
- Each output channel can be individually learned, and each channel can remember 8 remote control buttons.
- EDRF01 supports interlocking (H4), self-locking (T4), and jog (M4) modes. Learning button triggering for learning, channel setting, and mode conversion is easy.
- Support 4 channels of output, the module comes with learning indicator and VT data effective indication, the operation is more intuitive and convenient
- Built-in EEPROM supports up to 32 (8 per channel) remote control buttons
- Wide operating voltage range: 2V ~ 5.5V
- Module size: 18.8X14.8X5mm, small size, easier to install
Working Principle
- In the pulse data string of each frame learning code (eg EV1527) or fixed code (example PT2262), it is composed of two parts: address code and data code. Generally speaking, in the same remote controller, each button The address codes are the same, and the data codes of each button are different;
- In the EDRF01 module, after learning, the module is the address code and data code of the complete memory button;
- The module can intelligently identify the learning code or fixed code, and compares the address code and the data code of the key stored in the EEPROM from the received data string. If they are identical, the corresponding channel is output according to the corresponding working mode. .
Pin Definition
Pin name function description
- 1 GND power supply negative
- 2 VCC power supply positive
- 3 VT learning button input and decoding effective output, low output when decoding is valid
- Level, otherwise high impedance input state
- 4 D0 data output D0 channel
- 5 D1 data output D1 channel
- 6 D2 data output D2 channel
- 7 D3 data output D3 channel
Application
Wireless remote control switch, socket, wireless anti-theft alarm, wireless remote control door lock, wireless doorbell, wireless remote control electric shutter door and window, wireless LED lighting, industrial remote control products, etc.
Working Mode
Interlocking (H4)
Press the launch button, the corresponding one channel outputs a high level, all other channels are all low level, and remain until the next time the remote control data changes, and the valid signal is identified by determining the VT pulse;
Example: If the B key has been recognized by the D1 channel, press the B key. The D1 channel outputs a high level. All other channels are low. After releasing the button, the status of each channel remains unchanged.
Self-locking (T4)
The four channels are independent of each other and do not affect each other. Each time the transmitter button is pressed, the corresponding channel output state is inverted once, with VT pulse output;
Example: A key has been recognized by D2 channel learning. Whenever A key is pressed, the state of D2 channel is flipped once, and other channels are not affected.
Jog (M4)
Press the launch button, the corresponding channel outputs a high level, returns to low level after stopping the transmission, with VT pulse output;
Example: If the C key has been recognized by the D3 channel, press the C key. The D3 channel outputs a high level. When released, it returns to a low level. Other channels are not affected.
Use Guide
Pairing
In this version, the learning of the buttons and the setting of the channel have made significant improvements, and the operation is simpler and more convenient.
Example: I want to set a remote control button as the D0 channel of the control module. The specific operation is as follows:
Click the Learn button, then press and hold the remote button for more than 3 seconds in 6 seconds until the learning light flashes 2. This key is successfully learned and set to control the D0 channel.
If there are other buttons set to the same channel, within 6 seconds after the button is successfully set, just press and hold the button for more than 3 seconds until the learning indicator flashes 2 times.
The learning and setting methods of other channels are similar:
- D1 channel - tap 2 to learn button;
- D2 channel - tap 3 to learn button;
- D3 channel - Tap 4 to learn button.
(The remote control button coded memory is non-volatile memory EEPROM)
Switching Working Mode
- Long press the learning button for more than 0.5 seconds (0.5~1.5 seconds), after learning, the learning indicator flashes 2 times
- That is, enter the working mode transition state,
- Then you need to enter different modes according to the number of times you press the learning button within 6 seconds:
- If you press , enter H4 interlock mode;
- If you press 2, enter T4 self-lock mode;
- If you press 3, you will enter M4 jog mode;
- According to the need, after pressing the corresponding number of times, press and hold the learning button for more than 0.5 seconds (about 0.5~1.5 seconds, as a confirmation signal).
- After the hand is released, the learning indicator flashes 2 and the setting is successful and enters the corresponding working mode.
Clear Memory
- EDRF01 can store up to 32 remote control buttons (each channel can learn to recognize 8 buttons, 4 channels for a total of 32);
- When there are more than 8 channels per channel, the first key code learned will be overwritten;
- The way to clear the key code is:
- Press and hold the learning button for more than 4 seconds, and then the learning indicator flashes 2 times to successfully clear all the stored key codes;
- If the cleanup fails, repeat the above steps.
Specifications
- 1, working voltage: 2 ~ 5.5V
- 2, working current:
- ≈2.8mA (315MHz fully operational)
- ≈3.5mA (433MHz fully operational)
- 3, working frequency: 315MHz / 433.92MHz other frequencies can be customized
- 4, modulation method: ASK / OOK
- 5, receiving sensitivity: -108 dBm
- 6, data rate: up to 10kpbs
- 7, the driving capacity of each IO port: ≤ 20mA
- 8, working temperature range: -40 ~ 85 ° C