Category:AVR HDK
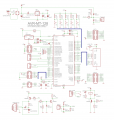
Development Board Schematic
Wiring
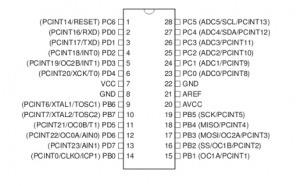
Pin Definition
This is the pins of ATmega168, a powerful chip and not expensive. You can also try to get even more cheaper ATmeaga 8A/8L or ATmega 328 version from us.
ISP Connector
For more information about the AVR ISP standard, please read this doc.
This is very important to make sure you find the right pin-1 of the ISP connector, otherwise you will waste a lot of time on testing connection but didn't find why, so just find the pin-1 correct.
Always make the 6 pins conntected, including:MISO, MOSI, Reset, VCC, GND, SCK, normally the programmer will provide power to the IC, so not necessary to provide extra power.
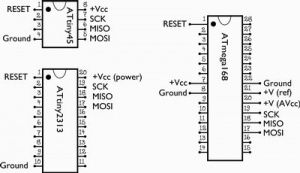
Pin configuration based on package
The General AVR package could be DIP-8, DIP-20, DIP-28, DIP-40
Many but not allof the AVR devices in a given package (e.g., DIP-8) share the same ISP connector pinouts, so these target boards can sometimes (with caution) even be used for different AVR microcontrollers. For example,the ATmega8, ATmega48, ATmega88, and ATmega168 share the same 28-pin pinouts. Note that in the figure above there are more than six connections to the ATmega168. That’s because there are extra power and ground lines running to the analog circuitry of the chip, which should be wired up even when the analog section is not in use.