ACS712
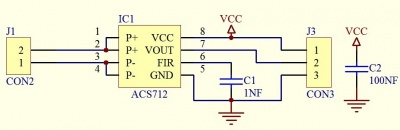
Schematic
- For redesigning this module, note to enlarge the trace line to accept the large current flow
How to Use
DC current measurement
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void loop() {
float average = 0;
for(int i = 0; i<= 1000; i++) { // sample 1000 times by 1 ms
average = average + (.0264 * analogRead(A0) -13.51);
delay(1);
}
Serial.print(average);
Serial.println("mA");
}
AC current measurement
Working Principle
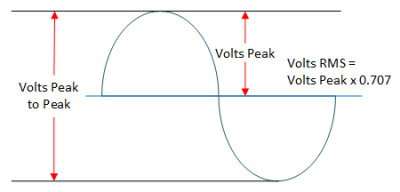
- Read the Vrms from the device:
Conversion for a sine wave with a zero volt offset (like your mains or line power) is performed as follows…
- Find the peak to peak voltage ( Volts Peak to Peak )
- Divide the peak to peak voltage by two to get peak voltage (Volts Peak)
- Multiply the peak voltage by 0.707 to yield rms volts (Volts RMS)
- First read Vrms, then convert it to Arms:
AmpsRMS = (VRMS * 1000)/mVperAmp;
- in which:
int mVperAmp = 185; // use 100 for 20A Module and 66 for 30A Module
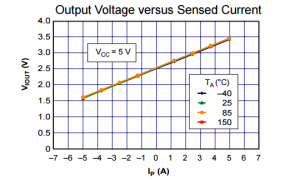
- The maximium output voltage is 3.5 for 5A, and 4.5 for 10A
Use Filiter Library
#include <Filters.h>
float testFrequency = 60; // test signal frequency (Hz)
float windowLength = 20.0/testFrequency; // how long to average the signal, for statistist
int sensorValue = 0;
float intercept = -0.1129; // to be adjusted based on calibration testing
float slope = 0.0405; // to be adjusted based on calibration testing
float current_amps; // estimated actual current in amps
unsigned long printPeriod = 1000; // in milliseconds
// Track time in milliseconds since last reading
unsigned long previousMillis = 0;
void setup() {
Serial.begin( 57600 ); // start the serial port
}
void loop() {
RunningStatistics inputStats; // create statistics to look at the raw test signal
inputStats.setWindowSecs( windowLength );
while( true ) {
sensorValue = analogRead(A0); // read the analog in value:
inputStats.input(sensorValue); // log to Stats function
if((unsigned long)(millis() - previousMillis) >= printPeriod) {
previousMillis = millis(); // update time
// display current values to the screen
Serial.print( "\n" );
// output sigma or variation values associated with the inputValue itsel
Serial.print( "\tsigma: " ); Serial.print( inputStats.sigma() );
// convert signal sigma value to current in amps
current_amps = intercept + slope * inputStats.sigma();
Serial.print( "\tamps: " ); Serial.print( current_amps );
}
}
}
Testing Results
- 220V 42W Home Fan (42/220 = 0.19)
Standby:
sigma: 0.98 amps: -0.00 sigma: 0.89 amps: -0.00 sigma: 2.76 amps: 0.07 sigma: 2.92 amps: 0.08
Running:
sigma: 2.86 amps: 0.08 sigma: 2.86 amps: 0.08 sigma: 2.93 amps: 0.08 sigma: 6.13 amps: 0.21 sigma: 6.00 amps: 0.20 sigma: 5.98 amps: 0.20
- 220V 13W Lamp (13/220 = 0.06)
sigma: 3.11 amps: 0.09 sigma: 3.12 amps: 0.09 sigma: 3.16 amps: 0.09
Simplified AC current measurement demo code
/*
Measuring AC Current Using ACS712
*/
const int sensorIn = A0;
int mVperAmp = 185; // use 100 for 20A Module and 66 for 30A Module
double Voltage = 0;
double VRMS = 0;
double AmpsRMS = 0;
void setup(){
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void loop(){
Voltage = getVPP();
VRMS = (Voltage/2.0) *0.707;
AmpsRMS = (VRMS * 1000)/mVperAmp;
Serial.print(AmpsRMS);
Serial.println(" Amps RMS");
}
float getVPP()
{
float result;
int readValue; //value read from the sensor
int maxValue = 0; // store max value here
int minValue = 1024; // store min value here
uint32_t start_time = millis();
while((millis()-start_time) < 1000) //sample for 1 Sec
{
readValue = analogRead(sensorIn);
// see if you have a new maxValue
if (readValue > maxValue)
{
/*record the maximum sensor value*/
maxValue = readValue;
}
if (readValue < minValue)
{
/*record the maximum sensor value*/
minValue = readValue;
}
}
// Subtract min from max
result = ((maxValue - minValue) * 5.0)/1024.0;
return result;
}