Difference between revisions of "A4988"
(No difference)
|
Latest revision as of 19:59, 12 May 2021
Connection
Power connections
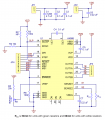
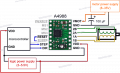
The driver requires a logic supply voltage (3 – 5.5 V) to be connected across the VDD and GND pins and a motor supply voltage (8 – 35 V) to be connected across VMOT and GND. These supplies should have appropriate decoupling capacitors close to the board, and they should be capable of delivering the expected currents (peaks up to 4 A for the motor supply).
Motor connections
Four, six, and eight-wire stepper motors can be driven by the A4988 if they are properly connected.
Step (and microstep) size
Stepper motors typically have a step size specification (e.g. 1.8° or 200 steps per revolution), which applies to full steps. A microstepping driver such as the A4988 allows higher resolutions by allowing intermediate step locations, which are achieved by energizing the coils with intermediate current levels. For instance, driving a motor in quarter-step mode will give the 200-step-per-revolution motor 800 microsteps per revolution by using four different current levels.
The resolution (step size) selector inputs (MS1, MS2, and MS3) enable selection from the five step resolutions according to the table below. MS1 and MS3 have internal 100kΩ pull-down resistors and MS2 has an internal 50kΩ pull-down resistor, so leaving these three microstep selection pins disconnected results in full-step mode. For the microstep modes to function correctly, the current limit must be set low enough (see below) so that current limiting gets engaged. Otherwise, the intermediate current levels will not be correctly maintained, and the motor will skip microsteps.
Micro-step Setup
| MS1 | MS2 | MS3 | Microstep Resolution |
|---|---|---|---|
| LOW | LOW | LOW | Full Step |
| HIGH | LOW | LOW | Half Step |
| LOW | HIGH | LOW | Quarter Step |
| HIGH | HIGH | LOW | Eighth Step |
| HIGH | HIGH | HIGH | Sixteenth Step |
Control inputs
Each pulse to the STEP input corresponds to one microstep of the stepper motor in the direction selected by the DIR pin. Note that the STEP and DIR pins are not pulled to any particular voltage internally, so you should not leave either of these pins floating in your application. If you just want rotation in a single direction, you can tie DIR directly to VCC or GND. The chip has three different inputs for controlling its many power states: RST, SLP, and EN. For details about these power states, see the datasheet. Please note that the RST pin is floating; if you are not using the pin, you can connect it to the adjacent SLP pin on the PCB to bring it high and enable the board.
Current limiting
To achieve high step rates, the motor supply is typically much higher than would be permissible without active current limiting. For instance, a typical stepper motor might have a maximum current rating of 1 A with a 5Ω coil resistance, which would indicate a maximum motor supply of 5 V. Using such a motor with 12 V would allow higher step rates, but the current must actively be limited to under 1 A to prevent damage to the motor.
The A4988 supports such active current limiting, and the trimmer potentiometer on the board can be used to set the current limit. One way to set the current limit is to put the driver into full-step mode and to measure the current running through a single motor coil without clocking the STEP input. The measured current will be 0.7 times the current limit (since both coils are always on and limited to 70% of the current limit setting in full-step mode). Please note that changing the logic voltage, Vdd, to a different value will change the current limit setting since the voltage on the “ref” pin is a function of Vdd.
Another way to set the current limit is to measure the voltage on the “ref” pin and to calculate the resulting current limit (the current sense resistors are 0.05Ω). The ref pin voltage is accessible on a via that is circled on the bottom silkscreen of the circuit board. The current limit relates to the reference voltage as follows:
Current Limit = VREF × 2.5
So, for example, if the reference voltage is 0.3 V, the current limit is 0.75 A. As mentioned above, in full step mode, the current through the coils is limited to 70% of the current limit, so to get a full-step coil current of 1 A, the current limit should be 1 A/0.7=1.4 A, which corresponds to a VREF of 1.4 A/2.5=0.56 V. See the A4988 datasheet for more information.
Power dissipation considerations
The A4988 driver IC has a maximum current rating of 2 A per coil, but the actual current you can deliver depends on how well you can keep the IC cool. The carrier’s printed circuit board is designed to draw heat out of the IC, but to supply more than approximately 1 A per coil, a heat sink or other cooling method is required.
Please note that measuring the current draw at the power supply will generally not provide an accurate measure of the coil current. Since the input voltage to the driver can be significantly higher than the coil voltage, the measured current on the power supply can be quite a bit lower than the coil current (the driver and coil basically act like a switching step-down power supply). Also, if the supply voltage is very high compared to what the motor needs to achieve the set current, the duty cycle will be very low, which also leads to significant differences between average and RMS currents.